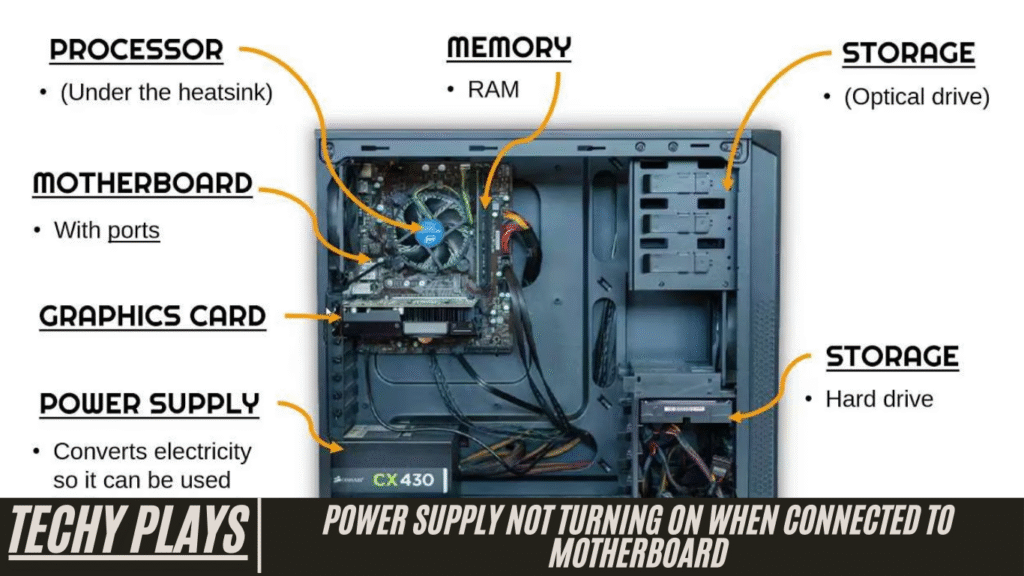
The power supply unit (PSU) is one of the most critical components of any computer system. Its primary function is to convert electricity from a standard wall outlet into usable power for all the internal components of your computer, including the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage devices, and peripheral components. Without a properly functioning PSU, your computer cannot operate, making it essential to ensure it works correctly at all times.
If your power supply isn’t turning on when connected to the motherboard, it can be a frustrating experience, especially when you are trying to power up your system. Before jumping to conclusions about hardware failure, there are several steps you can take to diagnose and potentially resolve the issue. First, always ensure all PSU connections are secure. This includes the 24-pin ATX motherboard connector, the CPU power connector (usually 4 or 8 pins), and any necessary GPU or peripheral power cables. Loose or improperly connected cables are one of the most common reasons a PSU fails to start.
Another effective step is to try pressing and holding the power button for 10 seconds. This can sometimes reset the motherboard’s power circuitry and help the PSU to initiate power delivery. Additionally, to isolate the issue, it is recommended to test the PSU on another computer if available. Doing so can help determine whether the problem lies with the PSU itself or with the motherboard or other components.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the common issue of power supplies not turning on when connected to the motherboard, exploring possible causes such as faulty connections, damaged cables, motherboard issues, or a defective PSU. We will also provide practical troubleshooting steps and solutions to help you quickly identify and fix the problem. By understanding how your PSU interacts with the rest of your system and knowing what to check when it fails to power on, you can save time, prevent further hardware damage, and ensure your computer runs smoothly.
Understanding Power Supply Failure
Experiencing a power supply failure in your computer can be frustrating and disruptive. The power supply unit (PSU) is responsible for delivering stable electrical power to all components, including the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and peripherals. When this critical component stops working, your computer may fail to boot, behave erratically, or shut down unexpectedly.
Power supply failure can occur for several reasons. Internal components may become damaged over time, wiring may degrade, or manufacturing defects could cause malfunction. External factors, such as unstable power from your electrical outlets, can also contribute to PSU issues. Understanding the root causes and recognizing early warning signs can help prevent permanent damage to your computer and ensure a reliable computing experience.
How Do I Know If My Motherboard Or Power Supply Is Bad?
Identifying whether the problem lies with your motherboard or power supply is essential for effective troubleshooting. Common signs of a failing motherboard or PSU include:
- The system fails to boot or shows no signs of power
- Peripheral devices such as keyboard, mouse, or fans receive no power
- Burning smells or unusual odors coming from the computer
- Unstable or erratic behavior, including unexpected shutdowns, reboots, or failure to power on
To accurately diagnose the issue, you can use a multimeter to test the voltage output of the PSU. Additionally, visually inspecting components for signs of damage, such as burnt capacitors or melted connectors, can help pinpoint the problem. By systematically checking both the motherboard and the PSU, you can determine which component requires repair or replacement, saving time and avoiding unnecessary costs.
Common Reasons For Power Supply Issues
Read more: Asus Motherboard Bluetooth Not Working – Resolve Issues!
1. Power Surges
One of the most common causes of PSU failure is power surges. Sudden spikes in electrical power can damage sensitive components within the power supply, leading to malfunctions or complete failure. To protect your computer from these dangerous fluctuations, it’s highly recommended to use surge protectors or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). These devices help stabilize the incoming electrical current and safeguard your system from unexpected surges.
2. Overheating
Overheating is another major factor that can compromise a power supply’s performance. When heat accumulates inside the PSU, it can disrupt electrical circuits, reduce efficiency, or even cause the unit to shut down unexpectedly. Ensuring proper ventilation, avoiding obstructed airflow, and keeping your computer in a cool environment are effective ways to prevent overheating. Regular monitoring of system temperatures and using high-quality fans can further enhance the PSU’s longevity.
3. Dust Buildup
Dust accumulation inside the power supply can block airflow and interfere with heat dissipation, worsening overheating problems. Over time, dust and debris can settle on internal components, leading to poor performance or complete failure. Periodic cleaning using compressed air or a soft brush is an essential maintenance step to keep the PSU operating efficiently. Regular cleaning not only prolongs the lifespan of the power supply but also contributes to the overall health and stability of your computer system.
Troubleshooting Steps To Pinpoint And Resolve The Issue
When your computer fails to power on, identifying the root cause is critical. Proper troubleshooting of the power supply unit (PSU) and motherboard can save time, prevent damage, and ensure your system returns to full functionality. The following steps provide a structured approach to diagnosing and resolving power-related issues.
1. Checking Power Connections
The first step in troubleshooting is to carefully inspect all power connections. This includes the 24-pin main power connector, the CPU power connector (usually 4 or 8 pins), and any additional power cables for GPUs or other peripherals. Loose or improperly connected cables are a frequent cause of a PSU not turning on. Ensure that every cable is securely connected to both the power supply and the motherboard. A thorough check can often resolve issues without the need for further testing.
2. Testing the Power Supply
If connections appear secure but the system still fails to power on, the next step is testing the PSU. A multimeter or a dedicated PSU tester can measure the voltage output of the power supply to confirm that it is delivering the correct levels of power. A PSU that is underperforming or failing may provide insufficient voltage, which can prevent the motherboard and other components from functioning properly. Ensuring that your PSU meets the required specifications is essential before considering replacement or further troubleshooting.
3. Inspecting the Motherboard
After verifying the PSU, it is important to inspect the motherboard for signs of damage. Look for burnt or damaged components, bulging or leaking capacitors, or any loose connections. Additionally, ensure that all installed components, such as RAM, CPU, and expansion cards, are properly seated in their respective slots. A motherboard with visible damage or improperly seated components may prevent the PSU from supplying power correctly.
Psu Won’t Turn On When Connected To Mobo
If your PSU won’t turn on when connected to the motherboard, it typically indicates one of three possible issues: faulty power connections, a defective PSU, or motherboard problems. Begin troubleshooting by double-checking all connections and testing the power supply independently. If the PSU functions correctly, the motherboard may be the underlying cause. Diagnosing these issues methodically helps prevent unnecessary component replacements and ensures a targeted repair approach.
Power Supply Won’t Turn On When Connected To Motherboard
When a power supply doesn’t turn on after being connected to the motherboard, it can be a sign of underlying hardware problems. Always start by checking that all connectors are securely attached and that the PSU is delivering adequate power. Next, inspect the motherboard for damage or component failures. Testing components individually can pinpoint the issue, allowing you to resolve the problem efficiently and restore your system’s functionality.
PC Won’t Turn On, Power Supply Is Good. Is It The Motherboard?
If your PC fails to power on even though the power supply is confirmed to be working, the motherboard is likely the next component to evaluate. Check for visible signs of damage, such as burnt traces, bulging capacitors, or disconnected circuits. If no obvious issues are visible, consulting a professional technician or performing additional diagnostic tests may be necessary. In many cases, the motherboard is the key factor preventing the computer from powering on, even when the PSU is fully functional.
PC Does Not Start When Hitting Power Button Or Through Jump Starting The Motherboard
When your PC fails to start both by pressing the power button and through jump-starting the motherboard, it indicates that the issue may extend beyond just the power supply unit (PSU) or motherboard. In such cases, other components like the CPU, RAM, or even peripheral connections could be contributing to the problem. It’s important to systematically check each critical component, ensuring that they are properly seated, undamaged, and correctly connected to the motherboard. Sometimes, even minor issues, such as improperly installed RAM or a loosely connected CPU, can prevent the system from powering on.
My PSU Won’t Turn On When I Plug It Into The Motherboard
If your PSU doesn’t turn on after being plugged into the motherboard, it usually points to a potential issue with either the power supply itself or the motherboard. Start by verifying that all power cables are correctly connected and that the PSU is switched on. Testing the PSU independently with a multimeter or a PSU tester can confirm whether it’s delivering power correctly. If the PSU works outside the motherboard, the issue may lie with the motherboard or its power connectors.
Power Supply Doesn’t Turn On When Plugged Into The Motherboard
When the power supply fails to turn on after connecting it to the motherboard, it signals that either the PSU or the motherboard might be at fault. To troubleshoot, ensure all power connectors are firmly attached and test both the PSU and motherboard for possible faults. Proper troubleshooting is crucial to prevent replacing components unnecessarily and to pinpoint the exact cause of the problem.
Computer Not Powering On, Tested PSU Without Motherboard And Works Fine
If your computer isn’t powering on but the PSU works correctly when tested independently of the motherboard, the issue is likely with other components, such as the motherboard, CPU, or RAM. Additional diagnosis is required to identify the faulty component. This step helps narrow down the source of the problem, preventing wasted effort on components that are functioning properly.
Question – Help! Motherboard Not Working With PSU
If your motherboard is not working with the PSU, ensure that all connections are secure and properly seated. Test individual components, such as RAM, CPU, and expansion cards, to identify any faults. If the problem persists even after testing, it’s recommended to consult a professional technician for further diagnosis and resolution.
PSU Doesn’t Work Only When Connected To Motherboard
When the PSU works independently but fails when connected to the motherboard, it often indicates a problem with the motherboard or the connections between the PSU and the motherboard. Carefully inspect the connectors, reseat all cables, and test the system again. In some cases, a defective motherboard or misaligned pins can prevent the PSU from supplying power correctly.
New PSU Is Plugged In Motherboard But Won’t Turn On
If a new PSU is installed but the system won’t turn on, it suggests a potential issue with either the PSU or the motherboard. Ensure that all power connections, including the 24-pin main connector and CPU power connector, are correctly connected. If the problem persists, testing the PSU with a different motherboard can help determine whether the issue lies with the PSU or the motherboard itself.
My PC Is Not Turning On, But The PSU Works. What Should I Do?
If your PC doesn’t turn on even though the PSU is functioning correctly, start by verifying all connections to ensure nothing is loose or improperly seated. Test the PSU with another motherboard if possible, and inspect the motherboard for visible damage, burnt components, or faulty capacitors. If the issue persists, consulting a qualified technician is recommended for further diagnosis.
My PSU Works But My Motherboard Does Not Switch On
When the PSU is operational but the motherboard doesn’t turn on, common causes include faulty power connections, a malfunctioning motherboard, or damage due to power surges. Carefully inspect the motherboard for any visible damage and ensure all connections are secure before considering component replacement.
Motherboard Doesn’t Turn On Despite PSU Working Correctly
Even if your PSU is delivering power correctly, the motherboard may still fail to turn on. Possible reasons include defective circuits, improperly seated components, or damaged power connectors. Systematic troubleshooting of both the PSU and motherboard is essential to identify the exact cause.
Power Supply Not Turning On When Connected To Motherboard Windows
If your power supply does not turn on when connected to the motherboard in a Windows PC, it could indicate issues with the PSU, motherboard, or power connections. Performing a step-by-step troubleshooting process, including checking cables, testing the PSU, and inspecting the motherboard, is necessary to determine the underlying problem.
How To Check If Motherboard Is Receiving Power
To verify if your motherboard is receiving power, first ensure that all power connections are secure. Use a multimeter to test the voltage output from the PSU and confirm that it meets the required specifications. Additionally, inspect the motherboard for any signs of physical damage, burnt components, or loose connections. These checks help confirm whether the motherboard is receiving adequate power.
PC Power Supply Not Turning On
When your PC’s power supply fails to turn on, the issue could stem from faulty connections, PSU problems, motherboard malfunction, or sudden power surges. Careful troubleshooting is essential to identify the root cause and restore system functionality.
Motherboard Not Turning On
If your motherboard doesn’t power on, potential reasons include faulty connections, defective motherboard components, or insufficient power supply from the PSU. Systematic testing of all components is required to pinpoint the issue and implement the appropriate solution.
New PSU, But Still No Power
Even with a new PSU installed, if your system still does not power on, this suggests issues such as faulty connections, motherboard problems, or inadequate power delivery. Ensure all cables are properly connected and test the motherboard and other components to locate the source of the problem.
24-Pin Connector Not Working
The 24-pin connector is a crucial component that supplies power from the PSU to the motherboard. If this connector isn’t functioning properly, your motherboard may fail to receive adequate power, preventing your PC from turning on. Common issues include loose or improperly seated cables, bent pins, or physical damage to the connector itself. Always inspect the 24-pin connector for secure attachment and any visible damage before considering component replacement, as resolving this simple connection issue can often restore normal system functionality.
Motherboard Not Getting Enough Power
When the motherboard is not receiving enough power, it may fail to turn on or exhibit erratic behavior. This problem can arise due to several reasons, including a faulty PSU, damaged power cables, or using a power supply with insufficient wattage for your system’s requirements. Proper troubleshooting is essential to identify the root cause. Start by checking all power connections, ensuring that the PSU is capable of providing adequate wattage for your motherboard and installed components, and inspecting for any damaged or frayed cables.
Computer Won’t Power On…what Would I Test After Power Supply
If your computer still won’t power on after testing the PSU, the next step is to examine the motherboard and other critical components. Check for physical damage, loose or improperly seated components, and verify that all power connectors are properly attached. Inspect the CPU, RAM, and GPU to ensure they are securely installed and functioning correctly. Systematic testing of each component can help pinpoint the problem, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and avoiding unnecessary hardware replacements.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Why isn’t my power supply turning on?
If your power supply isn’t turning on, common causes include loose or faulty connections, a defective PSU, or damage from power surges. Begin troubleshooting by verifying that all connections are secure, the PSU switch is on, and using a multimeter or PSU tester to confirm functionality.
How to tell if power supply is bad or motherboard?
To determine whether the PSU or motherboard is faulty, inspect the system for abnormal behavior such as burning smells, unusual noises, or failure to power on. Testing the PSU with a multimeter and examining the motherboard for physical damage can help identify the faulty component.
How do I test if my PSU is failing?
Test a failing PSU by measuring voltage outputs with a multimeter, checking for overheating or burning smells, and observing abnormal behavior during operation. A PSU that fails to provide consistent power may need replacement.
How do I know if my motherboard PSU is fried?
If the motherboard PSU is fried, symptoms may include the system failing to turn on, burning odors, or visible component damage. Using a multimeter to check power delivery can confirm the issue.
My CPU is not starting. Power is going to the motherboard, but the fan switches off immediately. What is the solution?
This issue often indicates overheating, faulty power connections, or a defective CPU cooler. Inspect the CPU and cooler, ensure proper seating, and verify that power connections are secure to resolve the problem.
I’m building a PC: I installed my PSU, motherboard, and RAM. I plugged it in, turned it on, nothing happened. I turned it off, pulled the plug, and it shocked me. Is my motherboard fine?
If your PC does not turn on and you experienced a shock, there may be a problem with the motherboard or improper wiring. For safety and accuracy, seek professional assistance before further testing.
Why won’t my computer turn on after installing a new PSU? I tried installing the old PSU back but it didn’t work. The old PSU was 450W, and the new one is 500W. Did I do something wrong?
If your computer fails to power on after installing a new PSU, check compatibility, cable connections, and power settings. The increase in wattage is typically not an issue, but loose or incorrect connections may prevent proper startup.
My PC turns on and off by itself when the power button is connected to the motherboard. Is it the motherboard or power button/cable?
This behavior could be caused by a faulty power button, cable, or motherboard. Disconnect and reconnect the power button to troubleshoot, and if the issue persists, test the motherboard and cable independently.
Help! PSU won’t turn on when plugged into the motherboard.
If your PSU fails to turn on when connected, ensure all connections are secure, the PSU switch is on, and test the PSU with a multimeter. Faulty components or incorrect connections are often the cause.
Conclusion
In conclusion, troubleshooting power supply issues when connected to the motherboard requires a systematic approach. Start by checking all connections, inspecting the 24-pin connector, and verifying that the motherboard receives adequate power. Test the PSU independently, examine other components such as the CPU and RAM, and ensure compatibility with your system. Following these steps helps efficiently identify and resolve issues, ensuring optimal PC performance and preventing further hardware damage.